Tobacco causes 8 million deaths every year. When evidence was released this year that smokers were more likely to develop severe disease with COVID-19 compared to non-smokers, it triggered millions of smokers to want to quit tobacco. Quitting can be challenging, especially with the added social and economic stress that have come as a result of the pandemic, but there are a lot of reasons to quit.
Benefits of quitting tobacco
The benefits of quitting tobacco are almost immediate.
- After just 20 minutes of quitting smoking, your heart rate drops.
- Within 12 hours, the carbon monoxide level in your blood drops to normal.
- Within 2-12 weeks, your circulation improves and lung function increases.
- Within 1-9 months, coughing and shortness of breath decrease.
- Within 5-15 years, your stroke risk is reduced to that of a non-smoker.
- Within 10 years, your lung cancer death rate is about half that of a smoker.
- Within 15 years, your risk of heart disease is that of a non-smoker.
If that’s not enough here are a few more reasons!
Disadvantages of smoking
Adverse effects on appearance
- Everything stinks! From your skin, to your whole house,
- Tobacco causes teeth to yellow and creates excess dental plaque.
- Tobacco makes your skin wrinkly, making you look older faster. Smoking prematurely ages the skin by wearing away proteins that give the skin elasticity, depleting it of vitamin A and restricting blood flow.These wrinkles are more apparent around the lips and eyes and tobacco also makes skin leathery and dry.
- Tobacco smoking increases the risk of developing psoriasis, a noncontagious inflammatory skin condition that leaves itchy, oozing red patches all over the body.
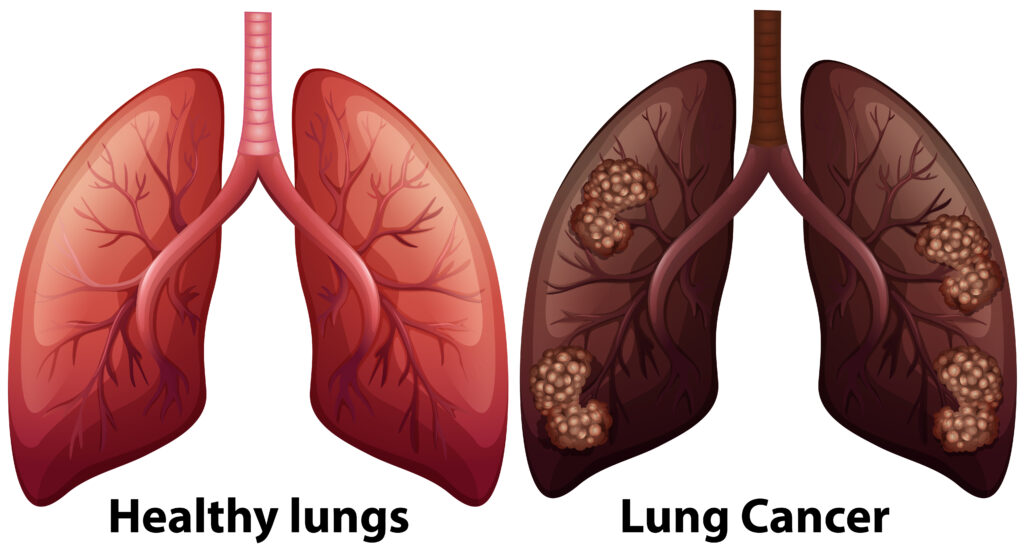
Cancer and death
- Tobacco use causes more than 20 types of cancer and is responsible for 25% of all cancer deaths globally.
- At least 70 cancer-causing chemicals are known in cigarette smoke.
- Smokers are at a significantly higher risk of developing acute myeloid leukaemia.
- Some studies have also demonstrated a link between tobacco smoking and an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Smoking and smokeless tobacco use cause oral cancer, cancers of the lips, throat (pharynx and larynx) and oesophagus.
- cancer of the nasal and paranasal sinus cavities.
- colorectal, kidney, liver, pancreatic, stomach or ovarian cancer.
- cancer of the lower urinary tract (including the bladder, ureter and renal pelvis).
Threats to the health of others
- More than 1 million people die from exposure to second-hand smoke each year.
- Non-smokers exposed to second-hand smoke are at risk of developing lung cancer and type 2 diabetes , also it may increase the risk of progression from tuberculosis infection to active disease.
- Cigarettes remain an important cause of accidental fires and resulting deaths.
Children at risk
- Smokers’ children suffer reduced lung function and inflammation of the airways.
- They are also at risk for asthma and chronic respiratory disorders in adulthood.
- Exposure of children to e-cigarette liquid continues to pose serious risks. There is a risk of the devices leaking, or of children swallowing the liquid also e-cigarettes have been known to cause serious injuries, including burns, through fires and explosions.
- Nicotine in e-cigarettes is a highly addictive drug that can damage the growing brains of children.
negative social consequences
- Tobacco use can affect social interactions and relationships negatively.
- Smokers spend an average of $ 1.4 million on personal expenses.
- This amount includes expenses related to smoking, medical expenses, etc.While they can spend it on more useful things.
- Tobacco use contributes to poverty by diverting household spending from basic needs.
- such as food and shelter to tobacco.
Sexual problems
- Smokers are more likely to experience infertility.
- Smoking restricts blood flow to the penis and causes erectile dysfunction.
- It changes the shape of sperm and reduces its number and motility in men.
Heart disease
- Just a few cigarettes a day or exposure to smoke increases the risk of heart disease.
- Smoking doubles the risk of stroke and quadruples the risk of heart disease.
- Tobacco smoke causes plaque to build up and blood clots to form. As a result, it restricts blood flow and eventually leads to heart attacks and strokes.
Impaired vision and hearing
- Evidence shows that smoking causes many eye diseases.
- Cataracts and glaucoma are among these diseases and can lead to blindness if left untreated.
- Smokers are more likely than non-smokers to develop age-related macular degeneration, a condition that results in irreversible vision loss.
Injury to all parts of the body
- Smoking is a major cause of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia.
- It is estimated that 14% of Alzheimer’s cases worldwide are related to smoking.
- Increases the risk of periodontal disease.
- Periodontal, a chronic inflammatory disease that destroys the gums and jawbone and leads to tooth loss.
- Smokers are at risk for diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s and bacterial meningitis.
Environmental pollution
- Tobacco pollutes the environment.
- Quit smoking to protect the environment.
- Cigarette butts are one of the most common garbage items collected on beaches and waterfronts around the world.
- Hazardous substances found in cigarette butts include arsenic, lead, nicotine and formaldehyde.
- Tobacco smoke can play a significant role in the level of air pollution in a city.
- Tobacco smoke contains three types of greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrogen oxides that pollute the environment.
- Deforestation for tobacco growing has serious environmental consequences.
- Consequences such as biodiversity loss, soil erosion and degradation, water pollution and increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
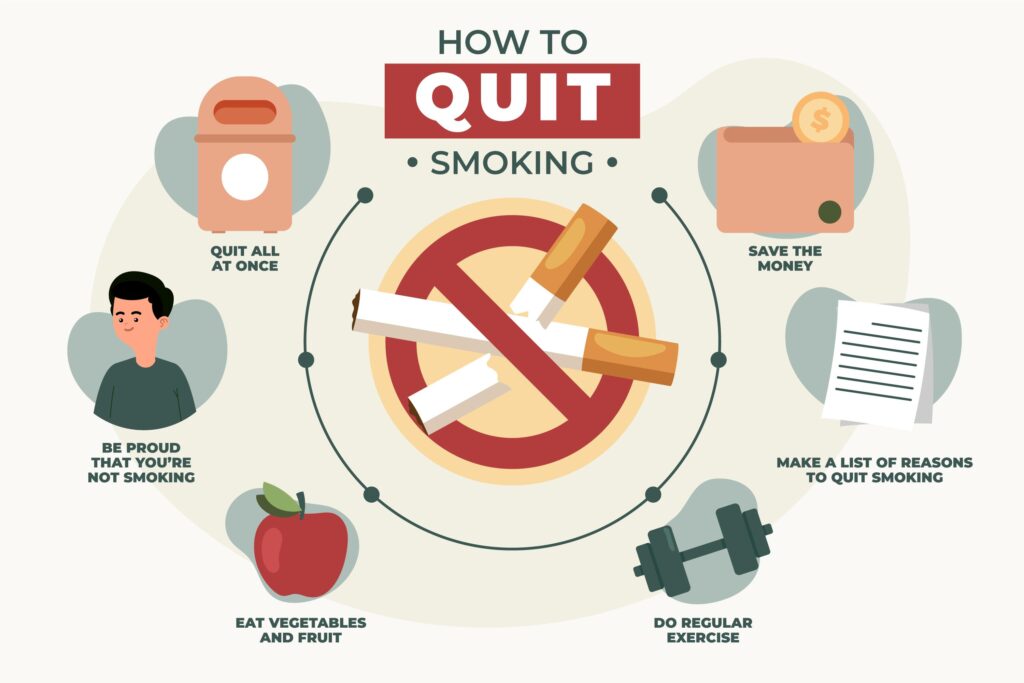
How to quit smoking
Quitting smoking is not an event that happens in one day, It is a journey.
By leaving them, you can improve your health and quality of your life and those around you.
Along the way, you need to change your behavior, manage it, and cope with the symptoms of nicotine withdrawal.
With proper planning, you can get rid of addiction and get rid of this habit forever.
Here are some ways to quit smoking:
- Set a date for departure and get ready
- Reduce your intake to the set date and stop it completely from the day you quit
- Tell your family and friends about your departure date
- Discard all cigarettes and cigarette butts
- Decide whether you are willing to use nicotine replacement therapy (NRT)
- If you want to join an addiction group, register now
- Use food substitutes such as candy, sugar-free gum, etc
- Ask friends and family who smoke , not to smoke around you, or stay away from them
- Drink plenty of water
- You will certainly smoke several times during the day, deal with it
- The urge to smoke lasts 3-5 minutes
- Distract yourself with other tasks
- Take a walk
- Take deep breaths and fill your lungs with fresh air
Sara Poursalehian – Medical engineering student
Resources : www.who.int & www.medicalnewstoday.com



